Web3 Explained: The Technology Changing the Internet
Web3: What does mean exactly?
Web3, also known as the decentralised web or the internet of value, refers to the use of blockchain technology and decentralised networks to build a new generation of internet applications. These apps aim to be more secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship compared to today’s centralised systems.
Web3 includes technologies such as decentralised finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs). These tools enable digital services that function without a central authority and give users greater control over their data, identity, and digital assets.
Most Web3 applications are built on decentralised blockchain networks like Ethereum. These networks maintain a shared, tamper-resistant record of transactions that anyone can verify. This makes it possible to create decentralised applications (dApps) that are globally accessible and operate without central servers.
Although Web3 is still evolving, it has the potential to transform the way we use the internet by redefining ownership, governance, and digital collaboration.
How is Web3 different from Web1 and Web2
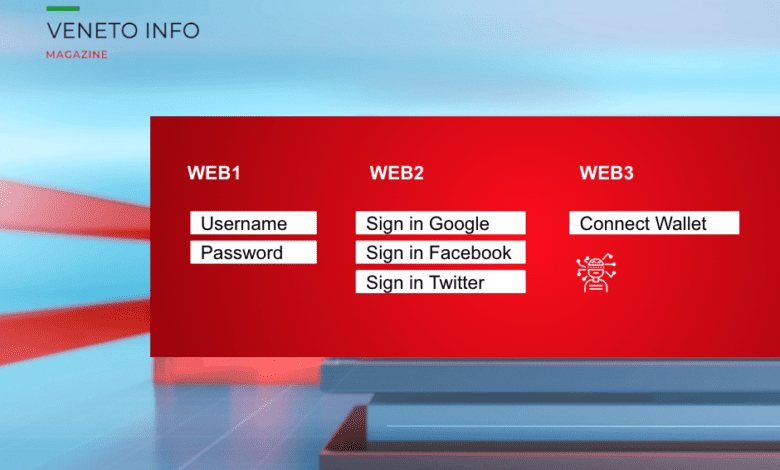
Web1, also called the static web, was the early internet made up of static HTML pages. Users could read information, but had almost no interaction.
Web2, known as the interactive web, brought dynamic websites, user-generated content, and platforms like social media and e-commerce. However, most services are controlled by large, centralised companies that collect and monetise user data.
Web3 aims to shift control back to users. It uses blockchain and decentralised protocols to allow peer-to-peer interactions, open governance, and digital ownership.
In simple terms, Web1 was about reading, Web2 is about participation, and Web3 is about ownership.
How can Web3 change our lives
Web3 technologies could affect various aspects of digital life:
- Financial inclusion. DeFi allows people to access financial services like lending or trading without needing a traditional bank.
- Security and privacy. Blockchain can offer a transparent and secure system for recording transactions. However, users must protect their private keys and be aware of risks like phishing.
- Ownership of digital assets. NFTs allow users to truly own digital art, items, and content in a verifiable way.
- Community-based governance. DAOs enable decentralised decision-making, though they also raise questions about efficiency and legal responsibility.
- New ways of collaborating. Web3 can create global, trustless systems for cooperation and value exchange without central intermediaries.
While Web3 offers many possibilities, it also brings new responsibilities and risks for users.
Challenges and limitations
- Complexity. Wallets, private keys, and blockchain tools are still difficult for many users.
- Security. Bugs, scams, and unverified smart contracts can lead to permanent loss of funds.
- Partial decentralisation. Many so-called decentralised projects are still run by small teams.
- Environmental concerns. Some blockchains have high energy usage, though this is improving with newer technologies.
How to get started
- Learn the basics of blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralised systems using courses and guides.
- Choose a blockchain platform that suits your goals, such as Ethereum, Solana, or Polygon.
- Set up a digital wallet like MetaMask or Trust Wallet to store and manage cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
- Explore decentralised apps (dApps) to understand what kinds of services and communities exist.
- Be cautious. Do not share your private keys, and always research projects before getting involved.
Conclusion
Web3 represents a vision of a more open, user-controlled internet built on decentralised technologies. It promises to change how we interact online, from how we store value to how we govern digital spaces.
However, it is still an experimental space with unresolved legal, ethical, and technical issues. Whether becomes the foundation of the future internet or one of many alternatives, it is a development worth understanding and observing.
